
The topic for today is basic networking. How to build a functional network? What is a MAC or IP address? How a subnet mask determines what octet of an IP address is for the network or host. What is a switch and default gateway
What Is An IP Address?
The IP address is the identity of a host device. Every single host device connected to the network has it’s own IP address. Just like an email address, for example. You need an email address to send or receive emails and likewise a destination email address to send or receive emails from. An IP address works the same way by allowing each host device to send or receive packets on the network. Every host device that wants to communicate on the network has its own IP and MAC address. An IPv4 address is a 32-bit address, divided into 4 octets (parts). Each consisting of 8-Bits.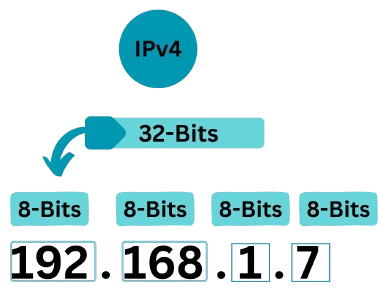
Subnet mask
The subnet mask determines which part (octet) of the IP address is network and which is host. So, for example, if a subnet mask starts as 255.255.255.0. This means that the fourth part (octet) is the host while the other three from the left are network. A visual example would be something like this.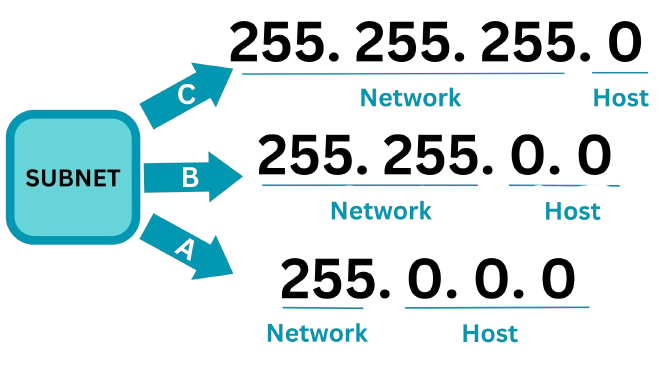 This is how a basic network is usually set up. However, a subnet mask can allow for multiple networks by borrowing octets from the host as well. That process is known as subnetting. Subnetting basically allows you to create more networks within a subnet by reducing the number of hosts you can have.
(Note: A host device can be a computer, a router, printer etc. Basically, anything that can communicate on the network has an IP address.
Note: IP packets are units of data sent over networks which can be the internet or other host devices such as a computer etc. Its data is divided into packets and sent over the network to the destination where it is compiled together by the end device.)
This is how a basic network is usually set up. However, a subnet mask can allow for multiple networks by borrowing octets from the host as well. That process is known as subnetting. Subnetting basically allows you to create more networks within a subnet by reducing the number of hosts you can have.
(Note: A host device can be a computer, a router, printer etc. Basically, anything that can communicate on the network has an IP address.
Note: IP packets are units of data sent over networks which can be the internet or other host devices such as a computer etc. Its data is divided into packets and sent over the network to the destination where it is compiled together by the end device.)
Why An IP address And Not A MAC Address?
A MAC address is unique to each host device as well. The MAC address never changes and is assigned by the hardware manufacturer, whereas the IP address is assigned by the ISP (internet service provider) and can be changed. However, both a MAC address and IP address are important when it comes to networking. Especially when it comes to troubleshooting or identifying devices physically. Conversely, to identify a device over a network, whether remote or the internet, you need an IP address. An IP address is easier to remember and change when shifting networks or making new ones. It’s easier to assign a unique IP address to each device over a network (Note: Since MAC addresses cannot be changed. They work as a unique physical identifier for the device connected to the network. This helps to locate the device physically when there are multiple devices on a single network. Note: Hypothetically speaking, even if it were possible to change the MAC address of a device, and it allowed for remote network connectivity, it would have been nearly impossible to work with when it came to multiple devices) Here is an visual example. To check the IP address and MAC address of a computer you can:
To check the IP address and MAC address of a computer you can:
- Open CMD -> Type -> Ipconfig /all ->Hit Enter
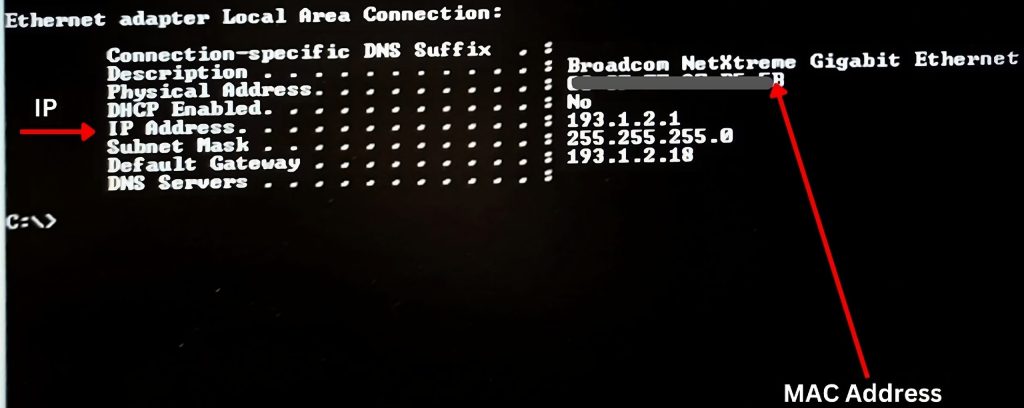 The Physical address is the MAC address and the IP address being the IP. However, in most computers that also support IPv6 it would be listed as “IPv4 Address” instead of just “IP Address” . In such instances unless you are using an IPv6 network. The IPv4 address would be the one to focus on.
The Physical address is the MAC address and the IP address being the IP. However, in most computers that also support IPv6 it would be listed as “IPv4 Address” instead of just “IP Address” . In such instances unless you are using an IPv6 network. The IPv4 address would be the one to focus on.
What Is A Switch? The Difference Between A Switch & A Router
The subnet mask determines which part (octet) of the IP address is network and which is host. So, for example, if a subnet mask starts as 255.255.255.0. This means that the fourth part (octet) is the host while the other three from the left are network. A visual example would be something like this.
A switch is a network device that connects host devices to each other over a single network. A normal layer 2 switch does not have an IP address. A layer 3 switch, however, can have one as it functions both as a switch and router. So, a basic layer 2 switch would just need physical connectivity to every host device that needs to communicate with each other.
Now a router, on the other hand, needs to be connected to the switch as well and has its own IP address. This IP address is the default gateway that every host device needs to have to be able to communicate with other networks connected to the router or the internet. So to check the IP address or change it. Connect your host device to the network and:- Open Network and Sharing Centre-> Connections->Your Network (Highlighted in Blue)
- Now Click-> Properties->Networking tab->Click Internet Protocol Version 4 (TCP/IPv4)-> Properties (below to the right)
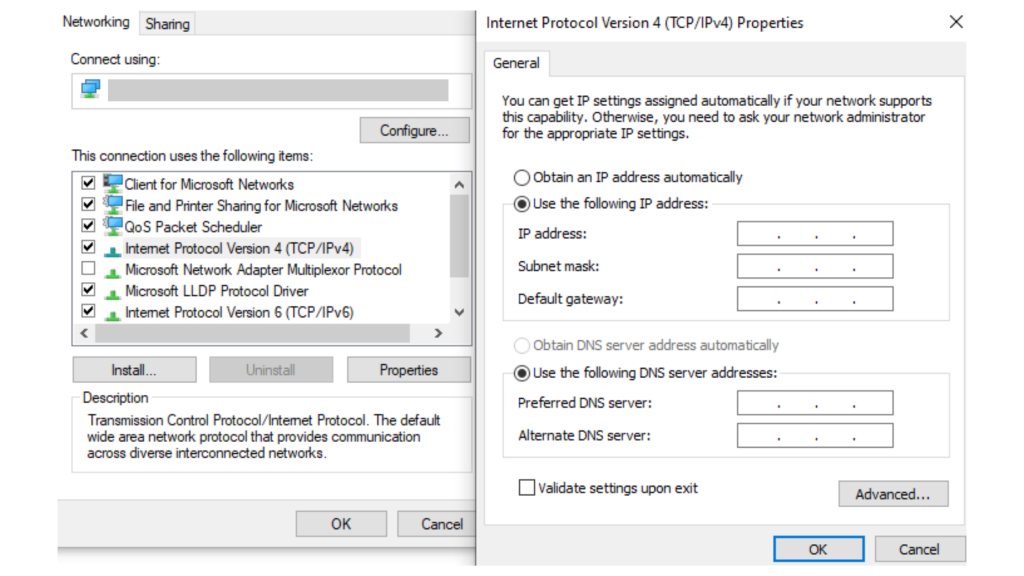
- Here you can add or change an existing IP Address, Subnet mask as well as default gateway.